Quixotic journeys often make for great literature, but by definition are rarely productive. I am, after all, referring to windmills here – not their 21st century creation, but their 17th century chasing. Futility, not productivity, was the ultimate fate of Cervantes’ man from La Mancha. So it is with hesitation, although quixotic obsession, that I plunge headlong into a discussion of American politics, healthcare legislation, resultant budget deficits and – finally – their potential effect on financial markets. There will be windmills aplenty in the next few pages and not much good can come of these opinions or my tilting in their direction. Still, I mount my steed, lance in hand, and ride forward.
Question: What has become of the American nation? Conceived with the vision of liberty and justice for all, we have descended in the clutches of corporate and other special interests to a second world state defined by K Street instead of Independence Square. Our government doesn’t work anymore, or perhaps more accurately, when it does, it works for special interests and not the American people. Washington consistently stoops to legislate 10,000-page perversions of healthcare, regulatory reform, defense, and budgetary mandates overflowing with earmarks that serve a monied minority as opposed to an all-too-silent majority. You don’t have to be Don Quixote to believe that legislators – and Presidents – often do not work for the benefit of their constituents: A recent NBC News/ Wall Street Journal poll reported that over 65% of Americans trust their government to do the right thing “only some of the time” and a stunning 19% said “never.” What most politicians apparently are working for is to perpetuate their power – first via district gerrymandering, and then second by around-the-clock campaigning financed by special interest groups. If, by chance, they’re ever voted out of office, they have a home just down the street – at K Street – with six-figure incomes as a starting wage.
What amazes me most of all is that politicians can be bought so cheaply. Public records show that combined labor, insurance, big pharma and related corporate interests spent just under $500 million last year on healthcare lobbying (not much of which went to politicians) for what is likely to be a $50-100 billion annual return. The fact is that American citizens have never been as divorced from their representatives – and if that description fits the Democratic Congress now in control – then it applies to Republicans as well – past and present. So you watch Fox, or is it MSNBC? O’Reilly or Olbermann? It doesn’t matter. You’re just being conned into rooting for a team that basically runs the same plays called by lookalike coaches on different sidelines. A “ballot box” pox on all their houses – Senators, Representatives and Presidents alike. There has been no change, there will be no change, until we the American people decide to publicly finance all national and local elections and ban the writing of even a $1 check for our favorite candidates. Undemocratic? Hardly. Get on the internet, use Facebook, YouTube, or Twitter to campaign for your choice. That’s the new democracy. When special interests, even singular citizens write a check, it represents a perversion of democracy not the exercise of the First Amendment. Any chance that any of this will happen? Not one ghost of a chance. Forward Don Quixote, the windmills are in sight.
Distressed as I am about the state of American democracy, a rational money manager cannot afford to get mad or “just get even” when it comes to investing clients’ money. Still, like pilots politely advertise at the end of most flights, “We know you have a choice of airlines and we thank you for flying ‘United’.” Global investment managers likewise have a choice of sovereign credits and risk assets where stable inflation and fiscal conservatism are available. If 2008 was the year of financial crisis and 2009 the year of healing via monetary and fiscal stimulus packages, then 2010 appears likely to be the year of “exit strategies,” during which investors should consider economic fundamentals and asset markets that will soon be priced in a world less dominated by the government sector. If, in 2009, PIMCO recommended shaking hands with the government, we now ponder “which” government, and caution that the days of carefree check writing leading to debt issuance without limit or interest rate consequences may be numbered for all countries.
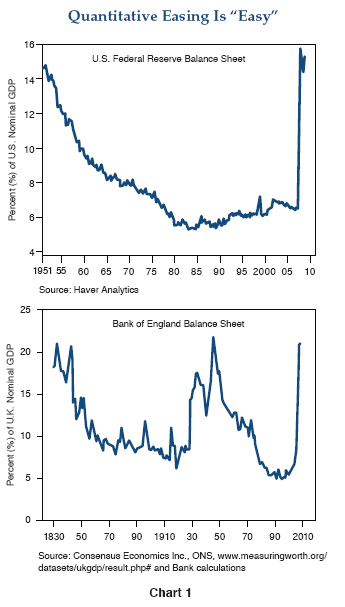
Explaining the current state of global fiscal affairs is often confusing – it’s much like Robert Palmer’s 1980s classic song where he laments that “She’s so fine, there’s no telling where the money went!” Where government spending has gone is not always clear, but one thing is certain: public debt is soaring and most of it has come from G7 countries intent on stimulating their respective economies. Over the past two years their sovereign debt has climbed by roughly 20% of respective GDPs, yet that is not the full story. Some of governments’ mystery money showed up in sovereign budgets funded by debt sold to investors, but more of it showed up on central bank balance sheets as a result of check writing that required no money at all. The latter was 2009’s global innovation known as “quantitative easing,” where central banks and fiscal agents bought Treasuries, Gilts, and Euroland corporate “covered” bonds approaching two trillion dollars. It was the least understood, most surreptitious government bailout of all, far exceeding the U.S. TARP in magnitude. In the process, as shown in Chart 1, the Fed and the Bank of England (BOE) alone expanded their balance sheets (bought and guaranteed bonds) up to depressionary 1930s levels of nearly 20% of GDP. Theoretically, this could go on for some time, but the check writing is ultimately inflationary and central bankers don’t like to get saddled with collateral such as 30-year mortgages that reduce their maneuverability and represent potential maturity mismatches if interest rates go up. So if something can’t keep going, it stops – to paraphrase Herbert Stein – and 2010 will likely witness an attempted exit by the Fed at the end of March, and perhaps even the BOE later in the year.
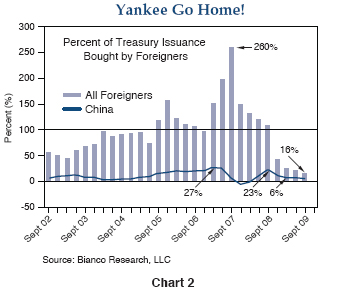
Here’s the problem that the U.S. Fed’s “exit” poses in simple English: Our fiscal 2009 deficit totaled nearly 12% of GDP and required over $1.5 trillion of new debt to finance it. The Chinese bought a little ($100 billion) of that, other sovereign wealth funds bought some more, but as shown in Chart 2, foreign investors as a group bought only 20% of the total – perhaps $300 billion or so. The balance over the past 12 months was substantially purchased by the Federal Reserve. Of course they purchased more 30-year Agency mortgages than Treasuries, but PIMCO and others sold them those mortgages and bought – you guessed it – Treasuries with the proceeds. The conclusion of this fairytale is that the government got to run up a 1.5 trillion dollar deficit, didn’t have to sell much of it to private investors, and lived happily ever – ever – well, not ever after, but certainly in 2009. Now, however, the Fed tells us that they’re “fed up,” or that they think the economy is strong enough for them to gracefully “exit,” or that they’re confident that private investors are capable of absorbing the balance. Not likely. Various studies by the IMF, the Fed itself, and one in particular by Thomas Laubach, a former Fed economist, suggest that increases in budget deficits ultimately have interest rate consequences and that those countries with the highest current and projected deficits as a percentage of GDP will suffer the highest increases – perhaps as much as 25 basis points per 1% increase in projected deficits five years forward. If that calculation is anywhere close to reality, investors can guesstimate the potential consequences by using impartial IMF projections for major G7 country deficits as shown in Chart 3.
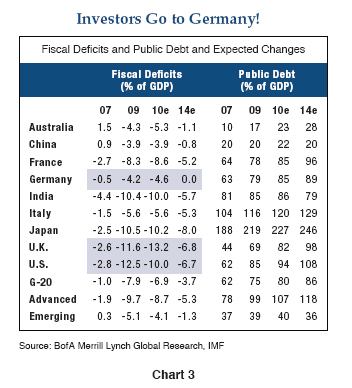
Using 2007 as a starting point and 2014 as a near-term destination, the IMF numbers show that the U.S., Japan, and U.K. will experience “structural” deficit increases of 4-5% of GDP over that period of time, whereas Germany will move in the other direction. Germany, in fact, has just passed a constitutional amendment mandating budget balance by 2016. If these trends persist, the simple conclusion is that interest rates will rise on a relative basis in the U.S., U.K., and Japan compared to Germany over the next several years and that the increase could approximate 100 basis points or more. Some of those increases may already have started to show up – the last few months alone have witnessed 50 basis points of differential between German Bunds and U.S. Treasuries/U.K. Gilts, but there is likely more to come.
The fact is that investors, much like national citizens, need to be vigilant and there has been a decided lack of vigilance in recent years from both camps in the U.S. While we may not have much of a vote between political parties, in the investment world we do have a choice of airlines and some of those national planes may have elevated their bond and other asset markets on the wings of central bank check writing over the past 12 months. Downdrafts and discipline lie ahead for governments and investor portfolios alike. While my own Pollyannish advocacy of “check-free” elections may be quixotic, the shifting of private investment dollars to more fiscally responsible government bond markets may make for a very real outcome in 2010 and beyond. Additionally, if exit strategies proceed as planned, all U.S. and U.K. asset markets may suffer from the absence of the near $2 trillion of government checks written in 2009. It seems no coincidence that stocks, high yield bonds, and other risk assets have thrived since early March, just as this “juice” was being squeezed into financial markets. If so, then most “carry” trades in credit, duration, and currency space may be at risk in the first half of 2010 as the markets readjust to the absence of their “sugar daddy.” There’s no tellin’ where the money went? Not exactly, but it’s left a suspicious trail. Market returns may not be “so fine” in 2010.
William Gross
Managing Director